Understanding the Bottleneck Rechner Optimize Your PC Performance
In the world of PC building and hardware optimization, one of the most debated and misunderstood concepts is the system bottleneck. When different parts of a computer—like the CPU, GPU, memory, or storage—don’t work in balance, one component can limit the performance of the whole system. That’s where a Bottleneck Rechner becomes invaluable: a tool to help you identify which component is holding your system back and guide smart upgrade decisions.
In this article, we’ll explain what the Bottleneck Rechner is, how it works, its limitations, and how you can put it to use to get the most from your computer.
What Does Bottleneck Rechner Mean?
“Rechner” is the German word for “calculator” or “computer,” so Bottleneck Rechner literally means “bottleneck calculator.” It refers to a tool—often an online service—that takes the specifications of your hardware (CPU, GPU, RAM, etc.) and estimates which part is most likely to limit performance under your desired use case (gaming, rendering, editing, etc.).
While many English-language sites call these tools “bottleneck calculators,” on a German site the term Bottleneck Rechner matches local language and expectations. The core goal remains the same: to show potential mismatches that may cause suboptimal performance.
Why Use a Bottleneck Rechner?
Before buying new components or upgrading hardware, you want to make sure that the money you spend actually improves performance. A Bottleneck Rechner helps in several ways:
-
Guided upgrade path
It highlights which component (CPU or GPU, perhaps memory) is underperforming relative to the rest. This prevents you from upgrading a part that already functions well, only to find the bottleneck shifts elsewhere. -
Balanced system planning
When building a PC from scratch, you can test various hypothetical combinations to see which pairings are more balanced. -
Performance prediction
For given workloads (gaming resolution, editing tasks), the Bottleneck Rechner can estimate whether your system will be limited by compute (CPU) or graphics (GPU). -
Avoiding wasted spending
Sometimes the limitation comes from RAM speed, storage throughput, or cooling, not the CPU or GPU. A calculator helps you see if your perceived “weak” component is actually significant in your scenario.
However, it’s not a magic bullet—there are important caveats.
How a Bottleneck Rechner Typically Works
A well-designed Bottleneck Rechner follows these general steps:
-
Component selection / input
You input or select your CPU model, GPU model, RAM configuration, and sometimes resolution (1080p, 1440p, 4K), desired settings, usage scenario (gaming, rendering, streaming). -
Database & benchmark data lookup
The Rechner refers to a database of benchmarks—frame rates, throughput, or performance metrics for many components under different tasks. -
Relative match and calculation
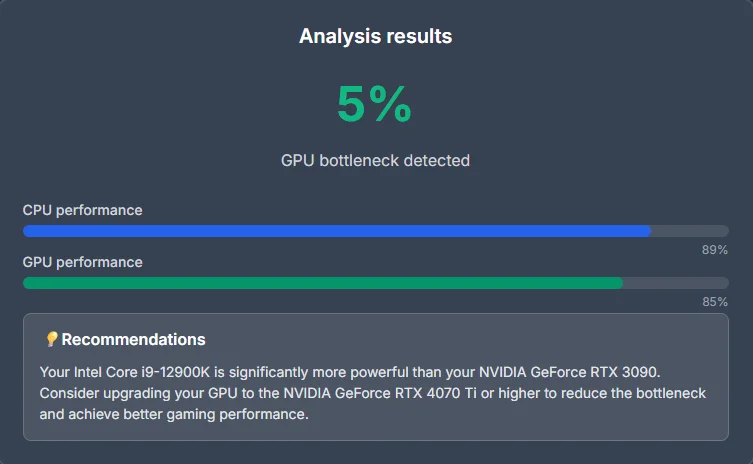
The tool compares performance potential of CPU vs GPU (or other parts) and computes a ratio or percentage indicating which side is more constrained. For example, if the CPU can produce 200 frames per second in a test but GPU can only output 150, it might say there is a 25% CPU bottleneck. -
Result & recommendation
The output often includes a “bottleneck percent” or category (e.g. negligible, moderate, severe) and suggestions (upgrade CPU, lower settings, etc.).
Some Bottleneck Rechner versions also consider RAM speed, storage speed, or other factors, but many stick to CPU vs GPU. HardwareDealz’s Bottleneck Calculator explains how they derive FPS benchmarks to compare performance.
The Limitations & Warnings Every User Should Know
While a Bottleneck Rechner is a helpful tool, it has limitations and potential pitfalls. It’s essential to use results as guidance—not absolute truth.
-
Scene-by-scene variability
In real games or workloads, the bottleneck may shift depending on what’s happening (AI, physics, particle effects). A single percentage can’t capture that dynamic behavior. -
Oversimplified models
Many calculators assume linear scaling or perfect conditions; they don’t always account for overhead, driver inefficiencies, thermal throttling, or software bottlenecks. -
Questionable accuracy
Critics argue these tools often produce misleading or exaggerated numbers. For instance, XDA Developers notes that bottleneck calculators are “vague, inaccurate, and can lead to unnecessary hardware purchases.” -
Ignoring non-obvious bottlenecks
Sometimes the limiting factor isn’t CPU or GPU but disk speed, cooling, power supply, or even software. -
False sense of security
Users might assume “5% bottleneck is safe,” but in practice, that 5% might still affect frames per second or responsiveness, depending on context.
Because of these, a Bottleneck Rechner should be used alongside real benchmarking tools (3DMark, Cinebench, real gameplay tests) as part of your decision process.
How to Use a Bottleneck Rechner Effectively
To get the best value from a Bottleneck Rechner, follow these tips:
-
Use accurate input data
Don’t guess your CPU, GPU, or RAM specs. Use system info tools (like CPU-Z or Device Manager) to input correct models. -
Choose your scenario carefully
Pick resolution, quality settings, and your intended tasks (e.g. 1440p gaming, video editing) when the Rechner allows it. Different scenarios may shift the bottleneck. -
Compare multiple Rechners
Use 2 or 3 different bottleneck tools and see if their conclusions match closely. If they diverge wildly, take those results with suspicion. -
Validate with real benchmarks
After you get a result, test your system under load (e.g. gaming or rendering) and monitor CPU & GPU utilization. If GPU stays at 100% while CPU is underused, the GPU is likely the limiting component. -
Make gradual upgrades
Use the calculator’s recommendations as guides. If it says your CPU is the bottleneck, upgrading to a stronger CPU or better cooling might help—but don’t overshoot. -
Re-run after changes
Whenever you upgrade or adjust a component, re-check with the Bottleneck Rechner to see how the system balance shifts.
Common Bottleneck Scenarios and What You Can Do
Here are some typical cases where a Bottleneck Rechner can help, and how to respond:
-
Powerful GPU, mid-range CPU
The calculator may show CPU limitations at 1080p or 1440p. Solution: upgrade CPU or reduce CPU-intensive settings, or match GPU with a more balanced CPU. -
High-resolution (4K) gaming
At 4K, GPU often becomes the bottleneck. The Rechner may show negligible CPU bottleneck. In such cases, upgrading GPU or lowering settings gives more benefit. -
Fast GPU + slow RAM
If your memory is slow or insufficient, your system could bottleneck at RAM. Some advanced Rechners include this factor. -
Thermal throttling or too high ambient temperature
If your CPU or GPU overheats and throttles, the performance drops artificially. No Rechner can fully account for real-world thermal conditions. -
Software-limited tasks
Workflow tools (e.g. video encoder, AI inference) might be bottlenecked by disk IO, single-threaded CPU paths, or storage speed — a Rechner focusing only on CPU/GPU may miss this.
Why a German Site Needs a Bottleneck Rechner
On a German domain like https://bottleneckrechner.de, offering a localized Bottleneck Rechner has several advantages:
-
Language & region alignment
German users will prefer localized tools with German labels and explanations, which improves comprehension and trust. -
Hardware relevance
Hardware popularity varies by region. A German Rechner can prioritize models common in the German / EU market. -
Educational resource
The site can also publish articles, guides, and tutorials in German about system bottlenecks, helping users interpret the results and avoid pitfalls. -
SEO advantages
Using native names like Bottleneck Rechner helps the site rank for German searches about bottleneck calculators.
So not only can the tool itself help users, but the site can become a hub of technical guidance tailored to German-speaking PC builders.
Conclusion
A Bottleneck Rechner is a powerful and practical tool for anyone wanting to optimize computer performance, particularly in PC building or upgrades. It helps highlight mismatched components (often CPU vs GPU), suggest upgrade paths, and guide balanced system design.
However, the tool is not flawless. Its estimates should be taken as directional—not absolute truths. Always cross-verify results with real benchmarking and system monitoring, and consider real-world factors like thermals, software, storage, and power.
If you run bottleneckrechner.de, combining a reliable calculator with helpful educational content and region-specific guidance can set your platform apart. Use the Bottleneck Rechner as the core tool, and supplement it with tutorials, case studies, and context to help users understand and apply the results wisely.